Income Inequality Trends in Sub-Saharan Africa: Divergence, Determinants and Consequences
Income Inequality Trends in Sub-Saharan Africa: Divergence, Determinants and Consequences
August 24, 2017
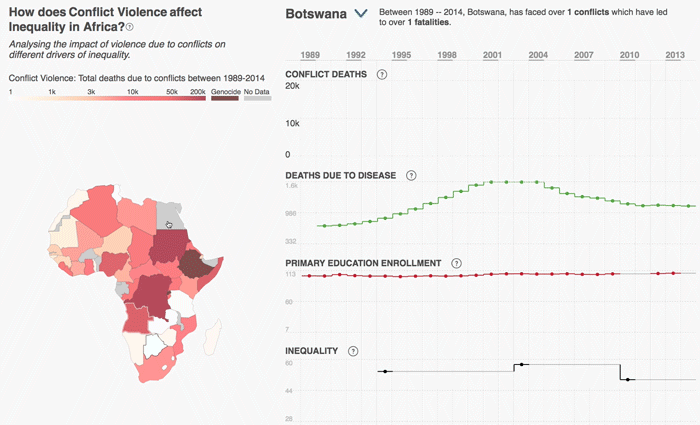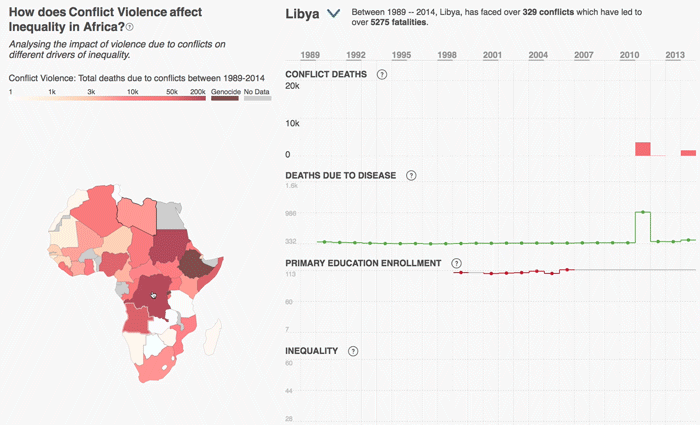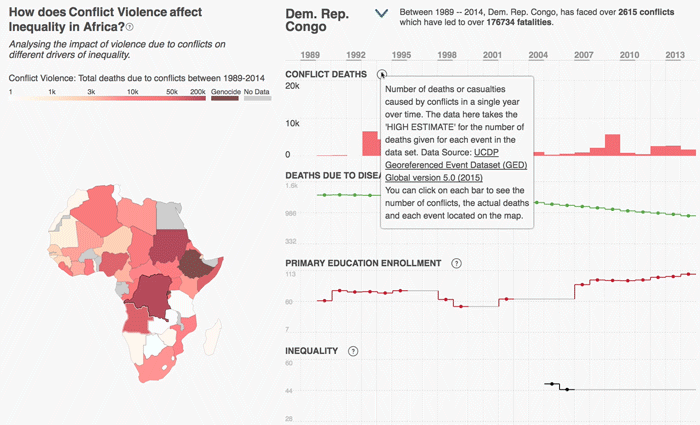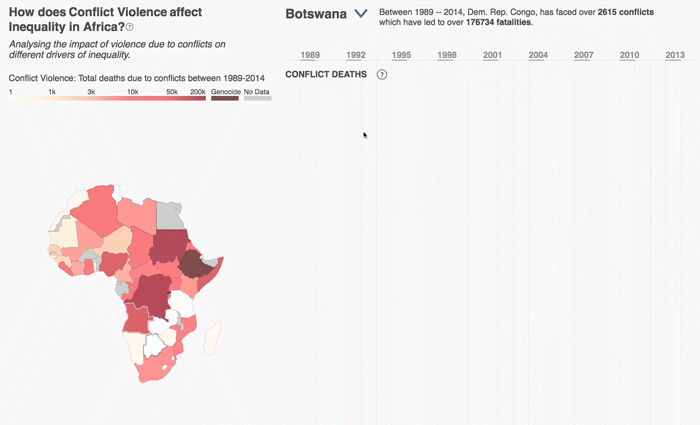
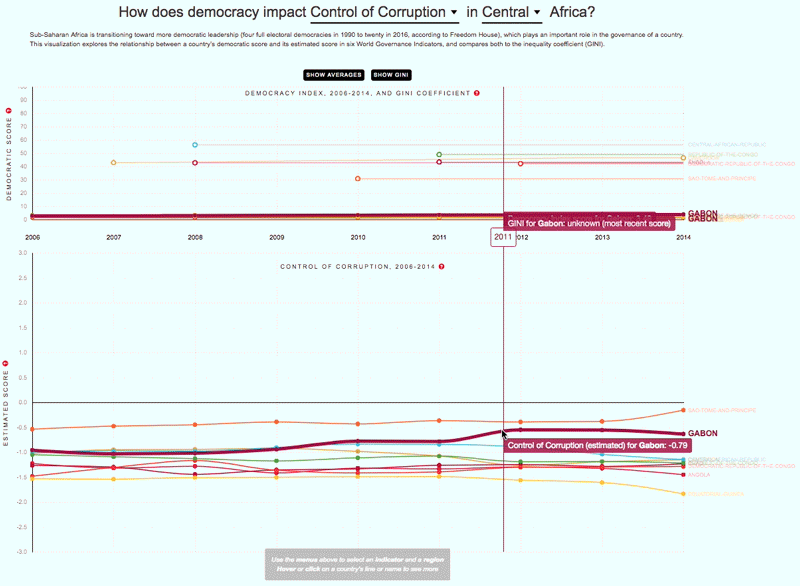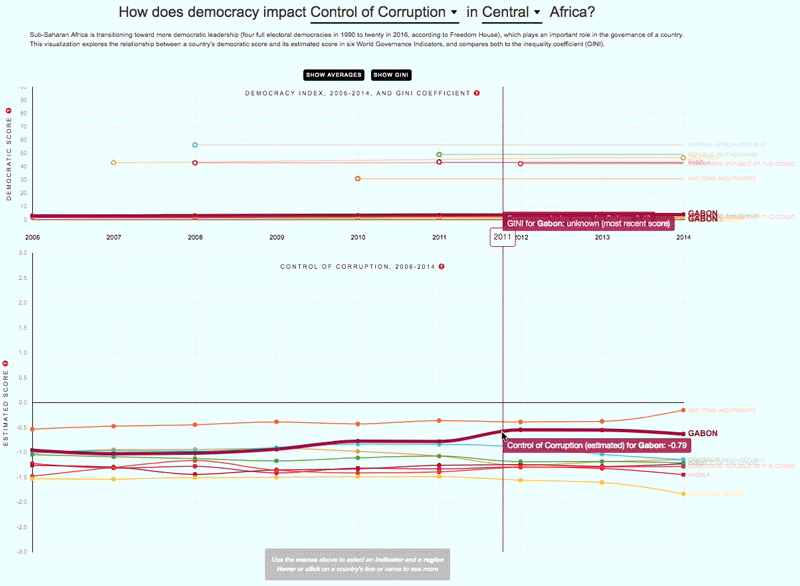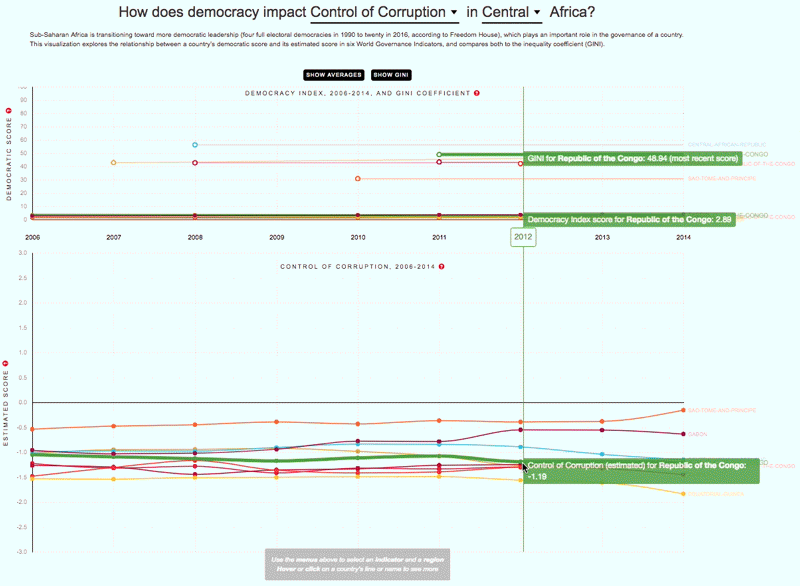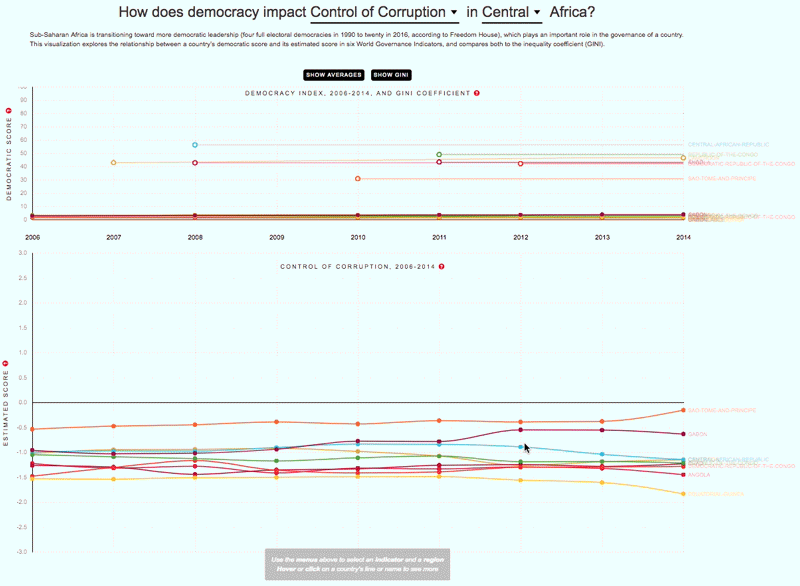
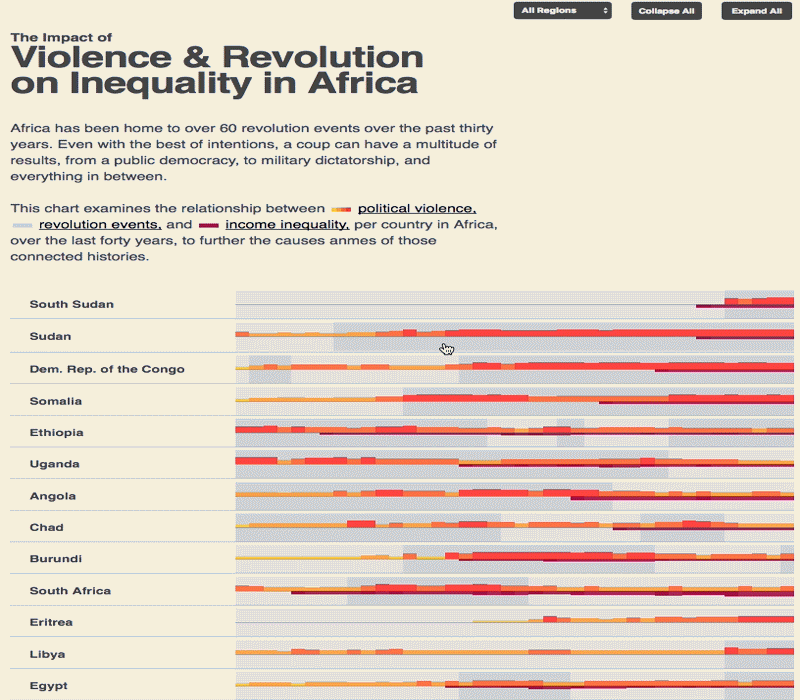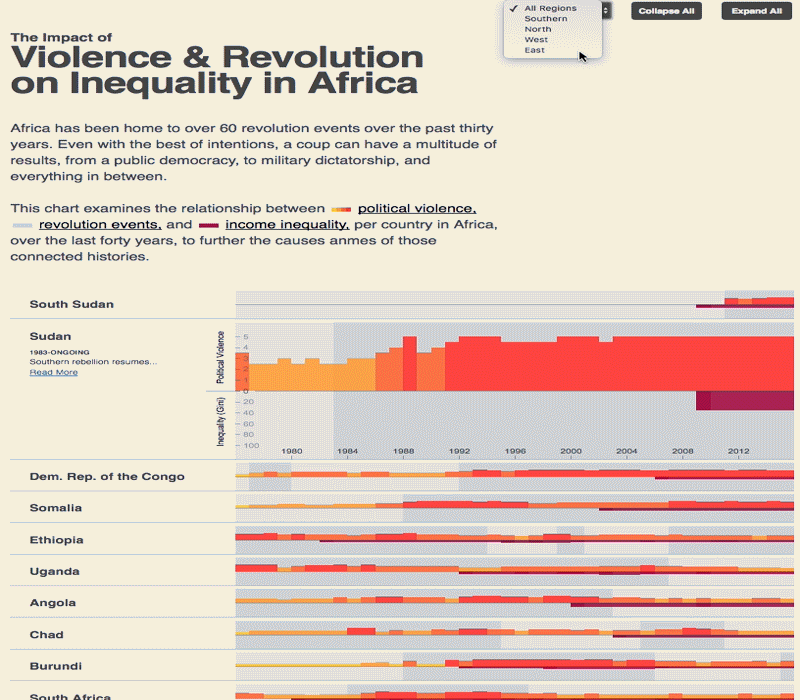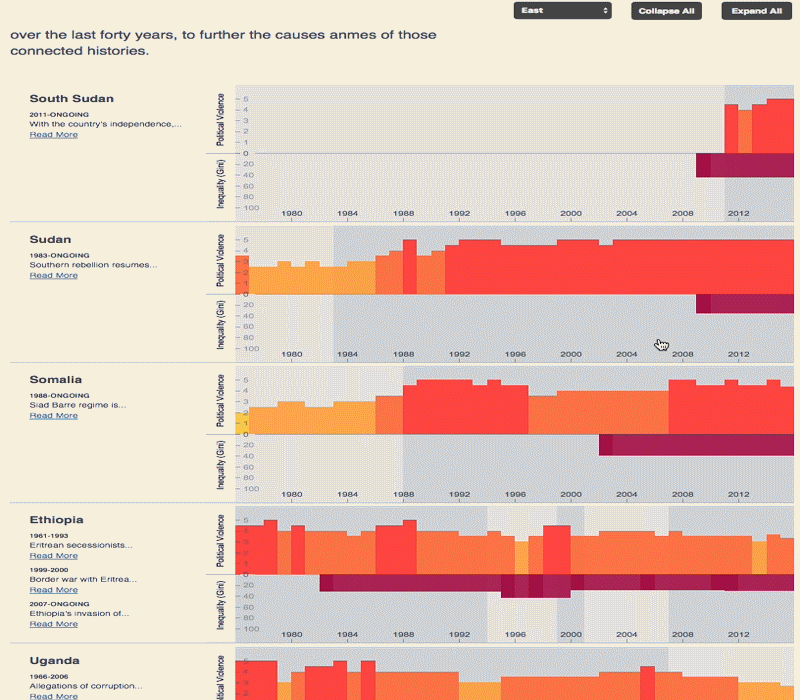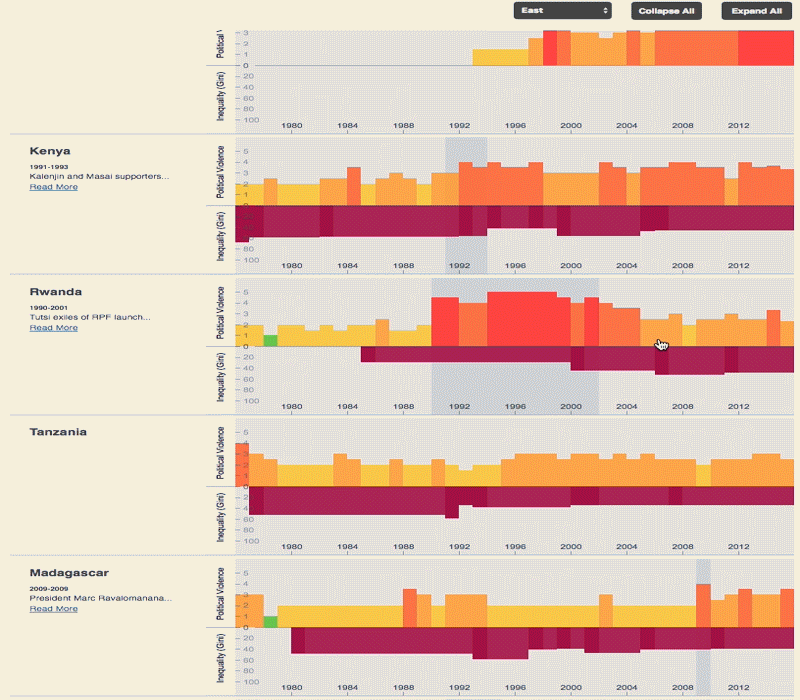
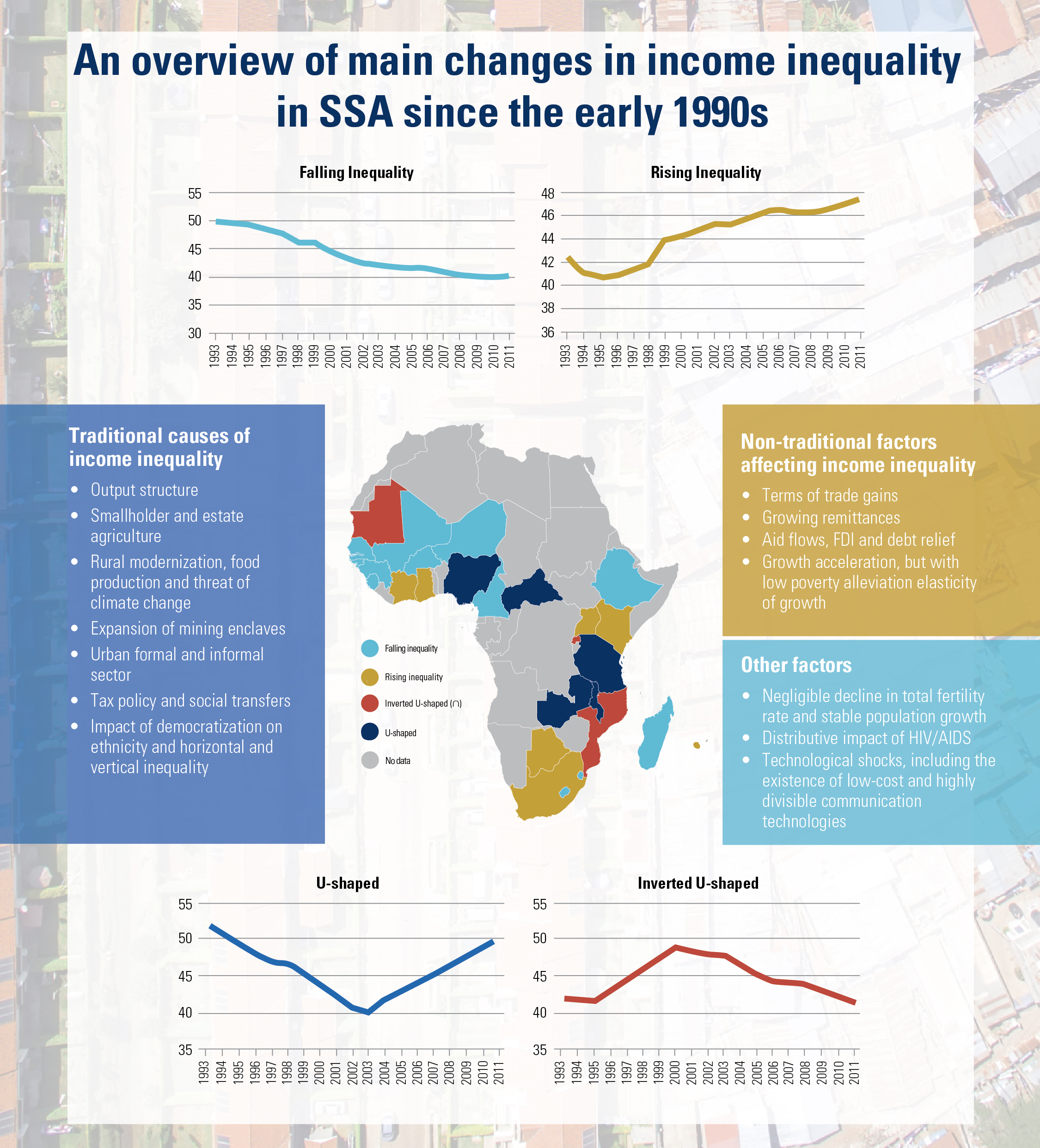
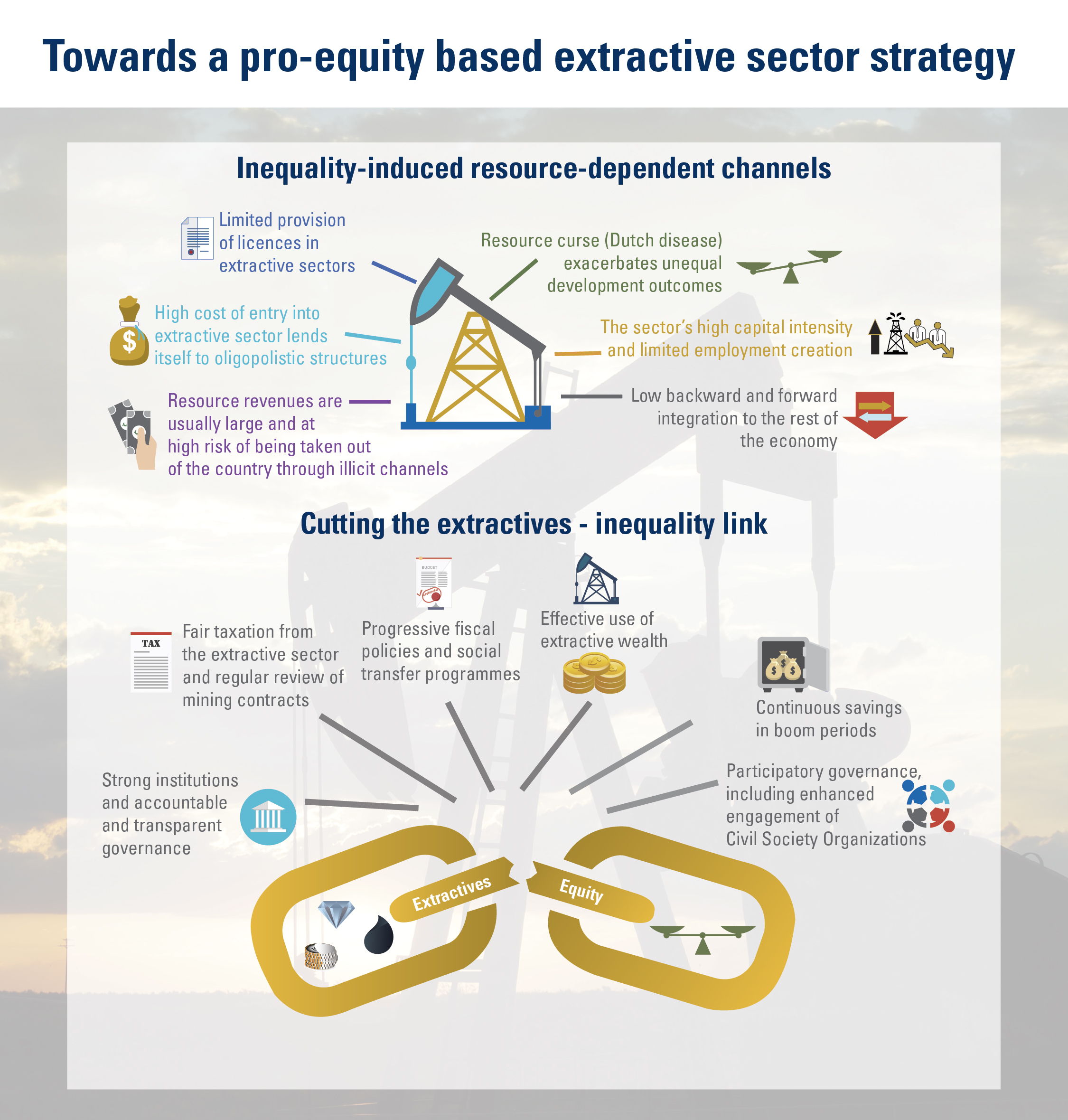
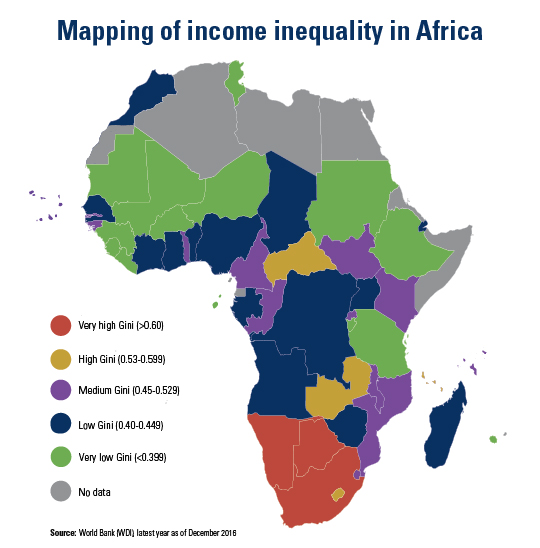
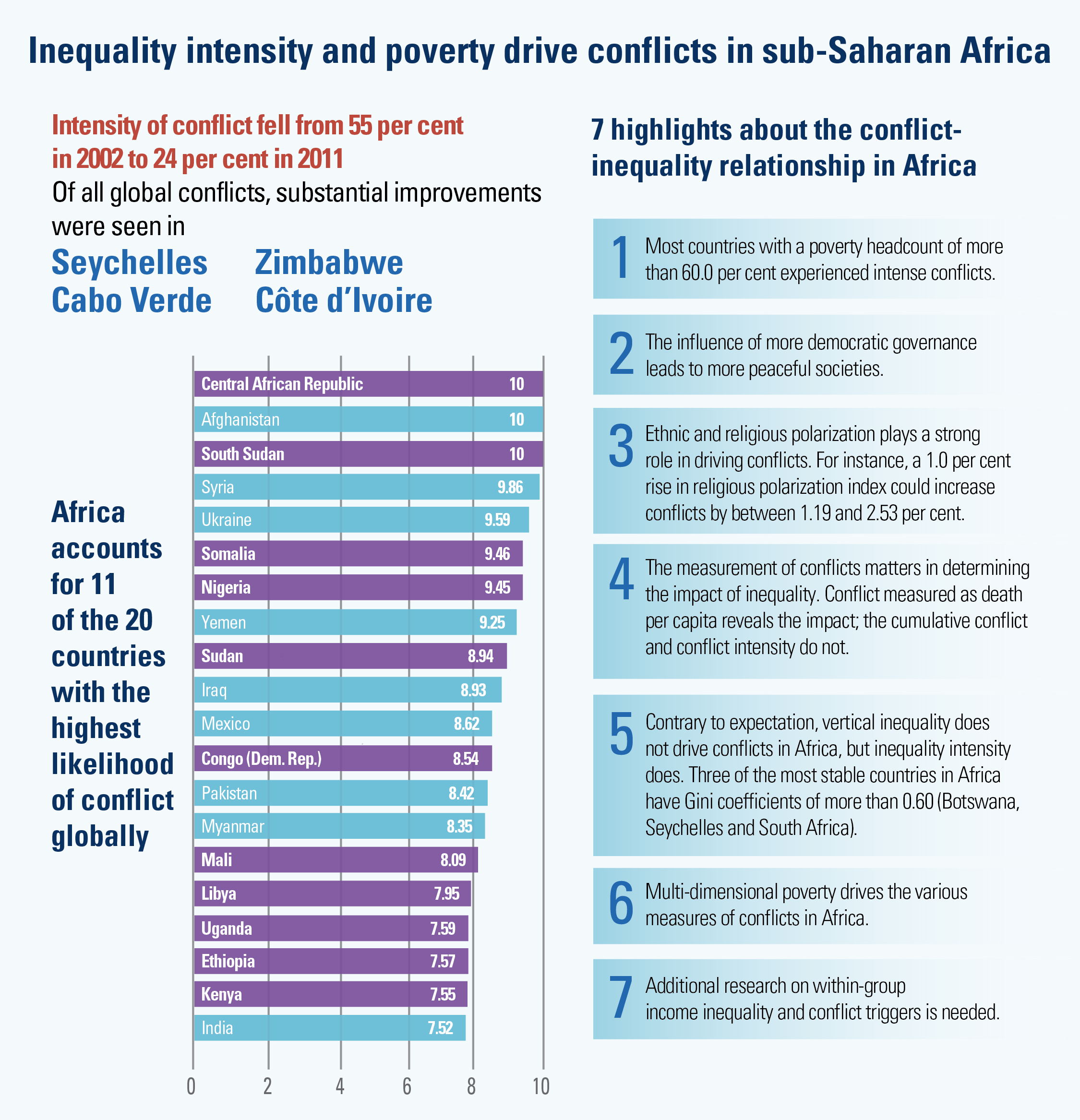
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and its 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) underscore the need to address broad inequalities in their quest to ‘leave no-one behind.’ Income Inequality Trends in sub-Saharan Africa: Divergence, Determinants, and Consequences is a groundbreaking United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) study that provides policy guidance to reduce income inequality in sub-Saharan Africa.
To achieve the goal of ‘leaving no one behind’ by 2030, UNDP's Regional Bureau for Africa asserts that inequality levels, trends,determinants and consequences must be analyzed closely – producing a holistic policy approach which matches the integrated and indivisible nature of the 2030 agenda. It is only through addressing the challenge of inequality that progress towards achieving poverty reduction, to be specific, and the SDGs in general, can be accelerated.
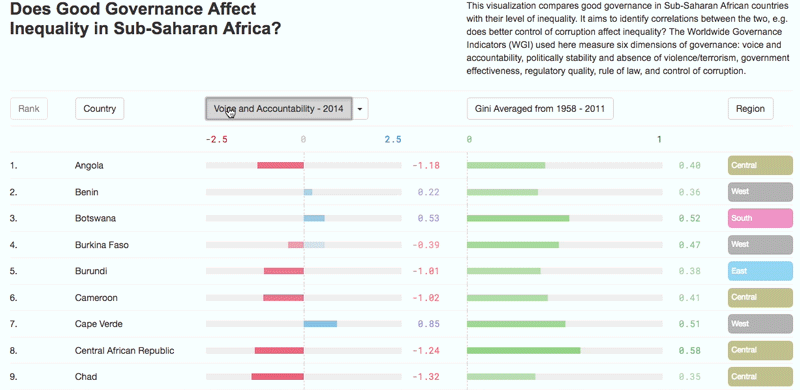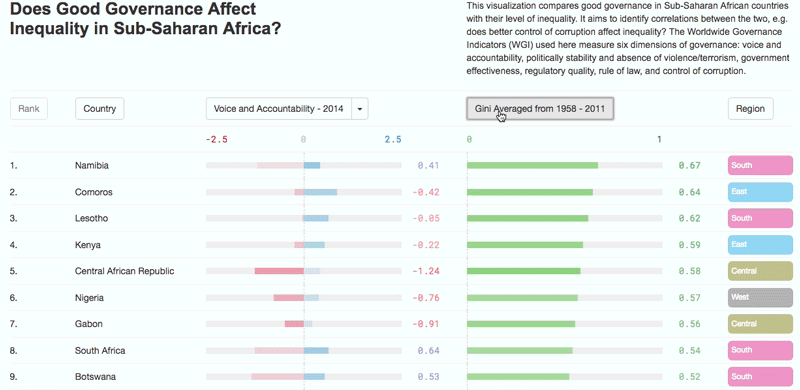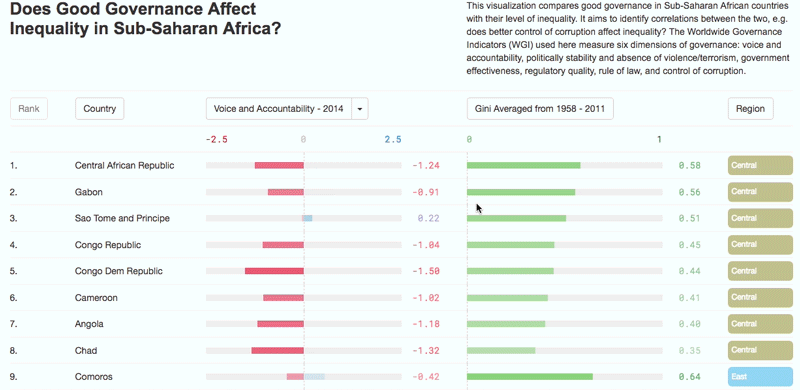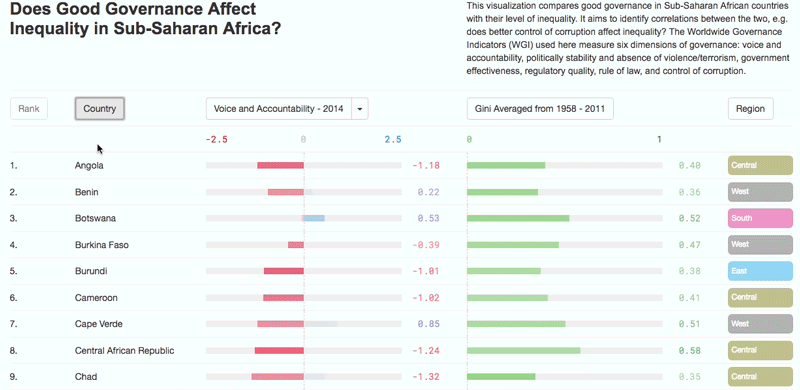
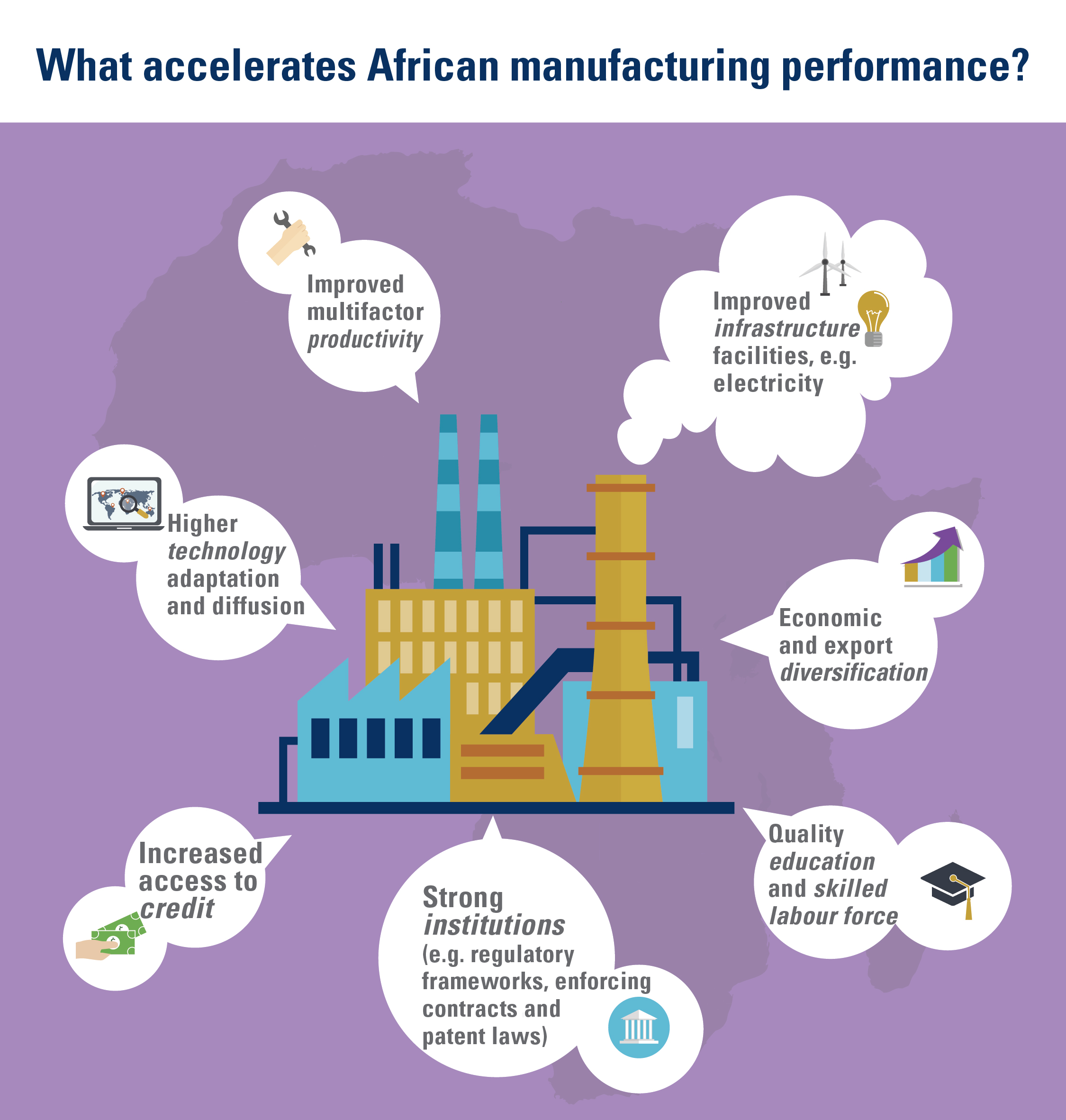
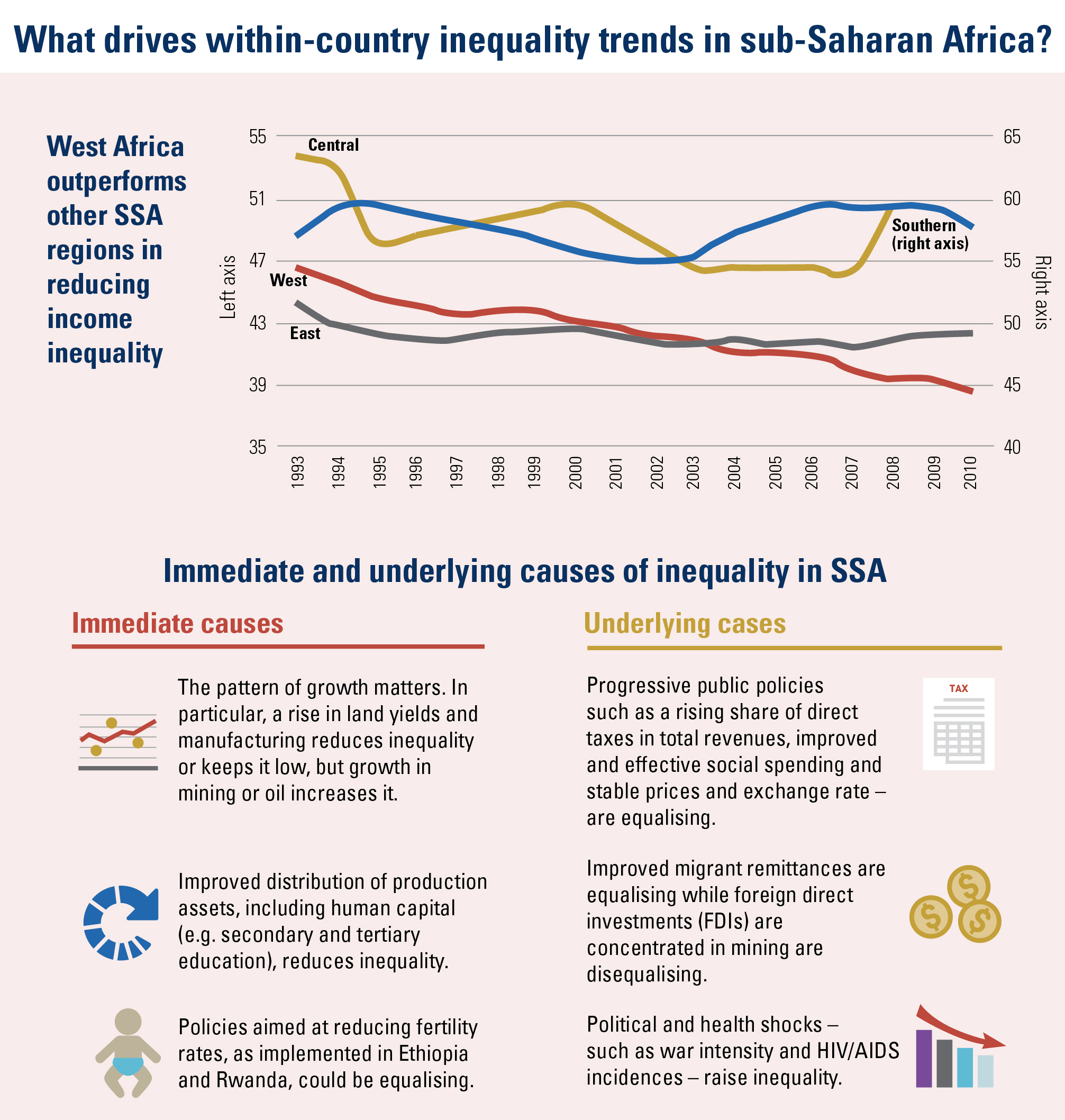
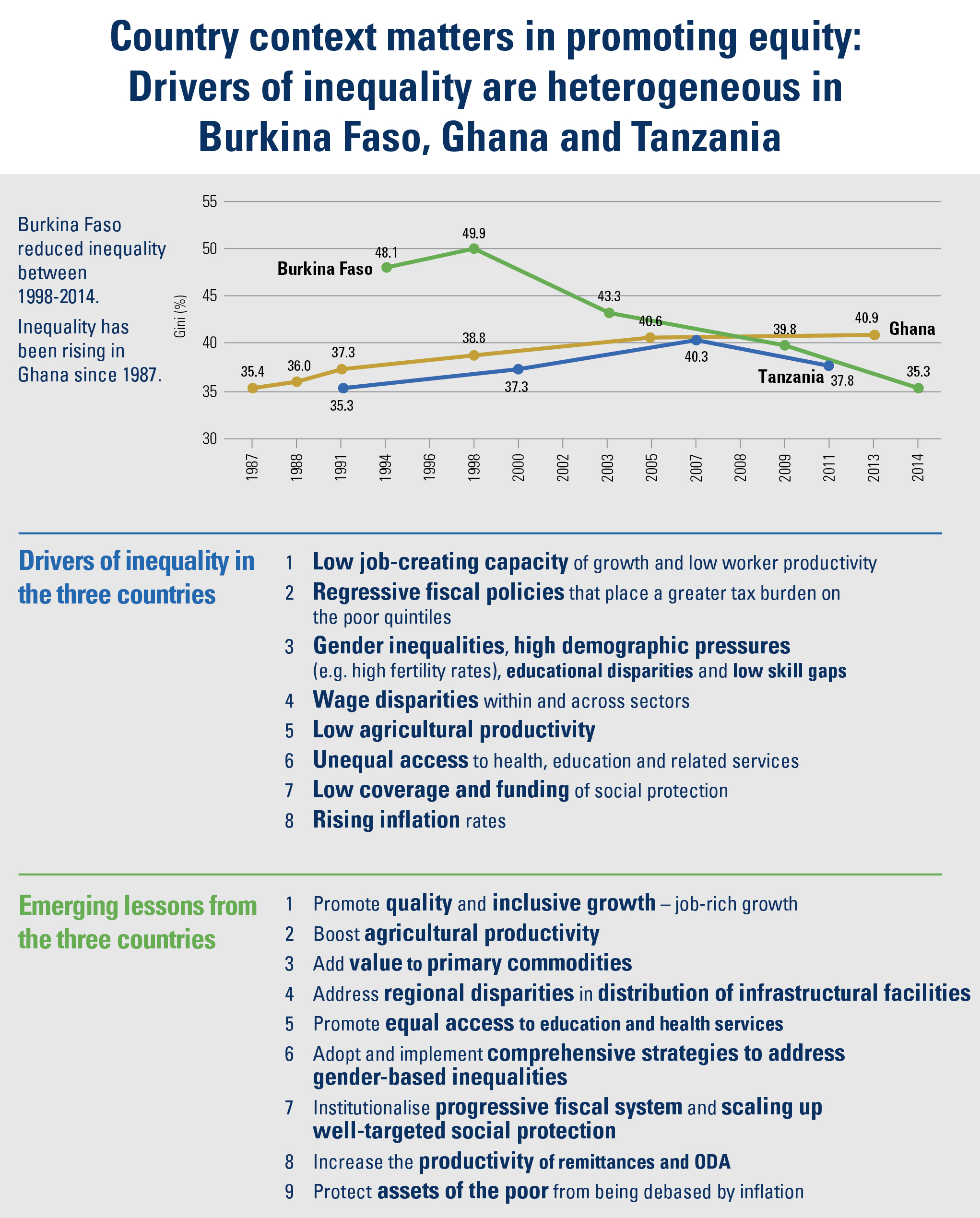
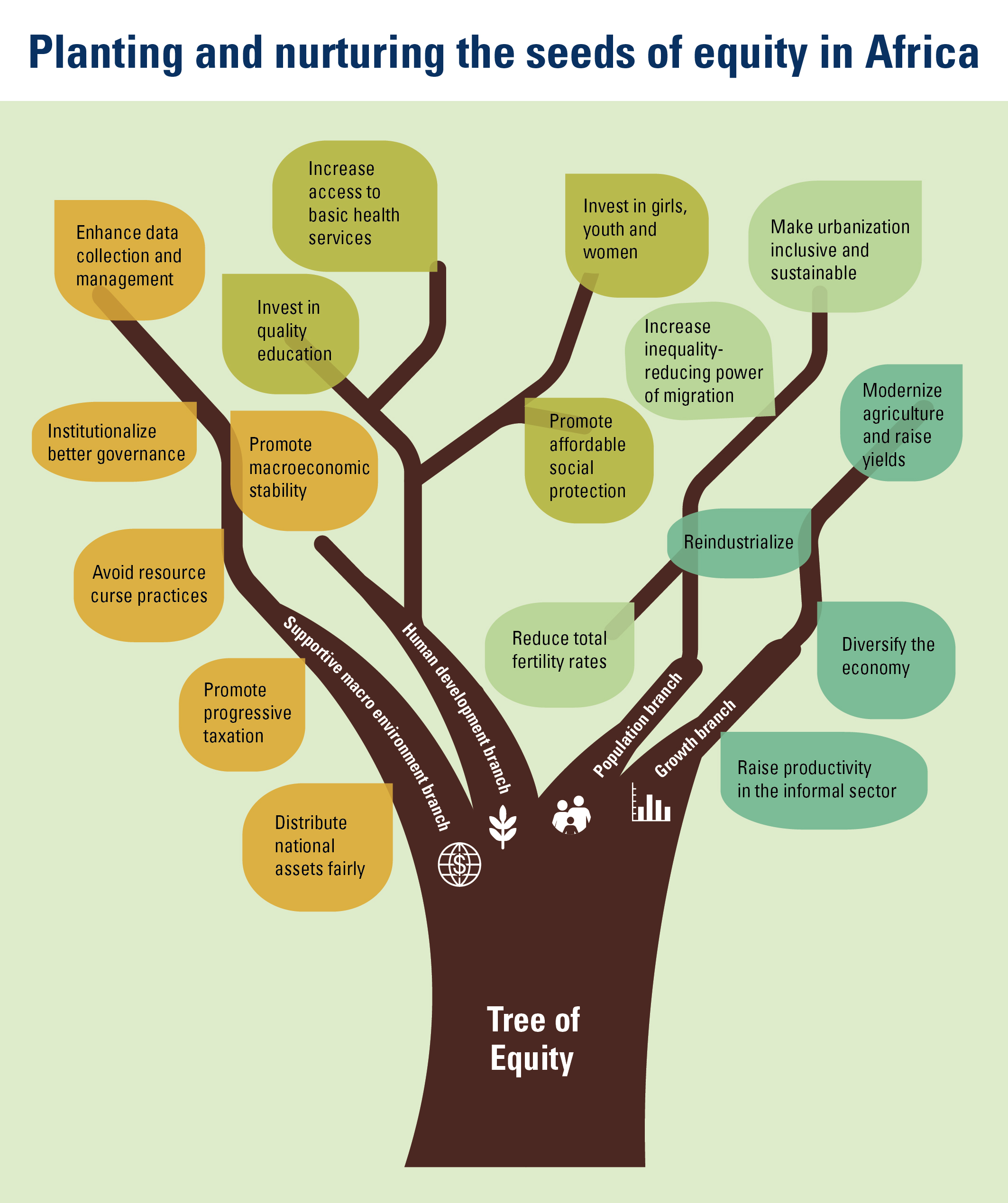
What factors decrease income inequality?
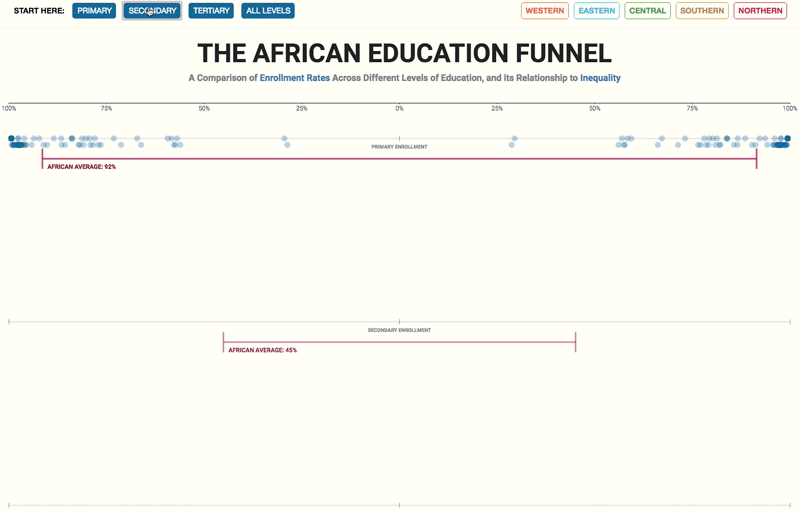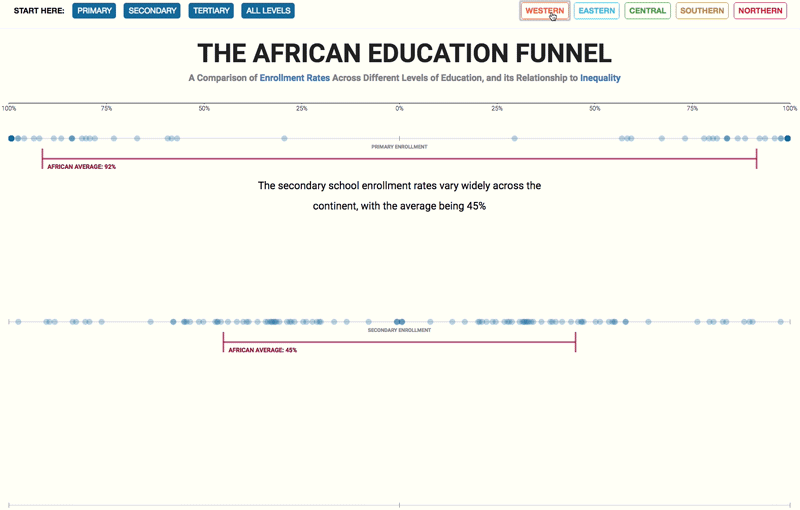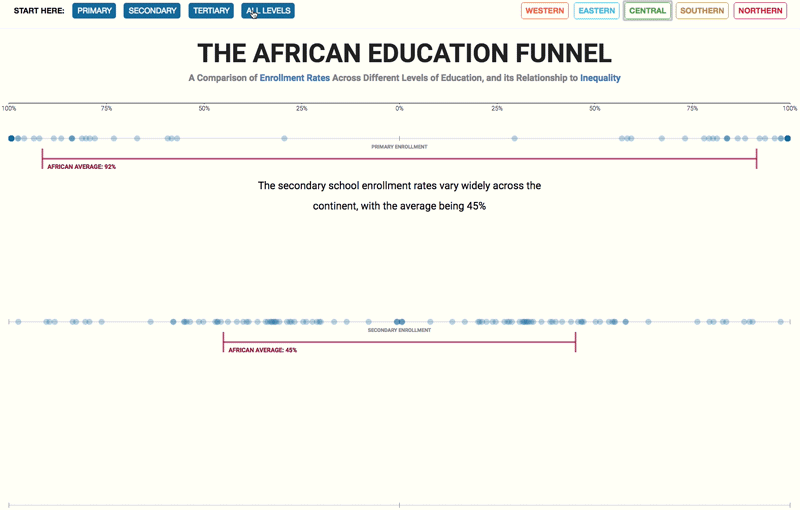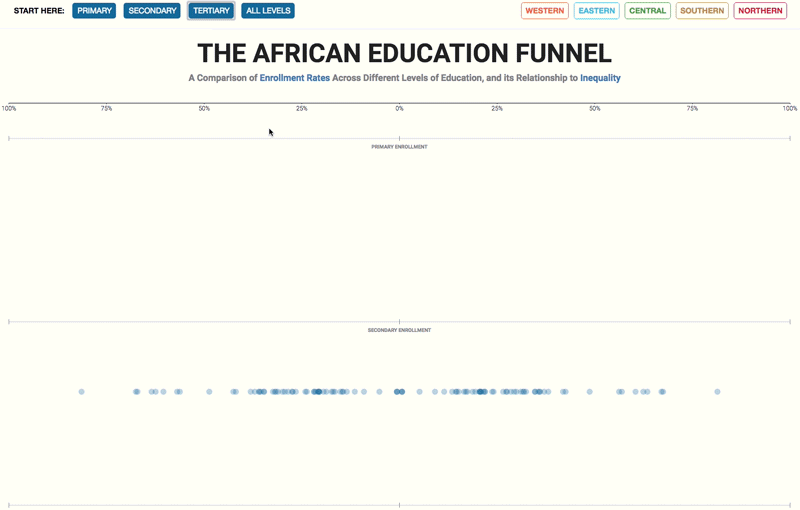
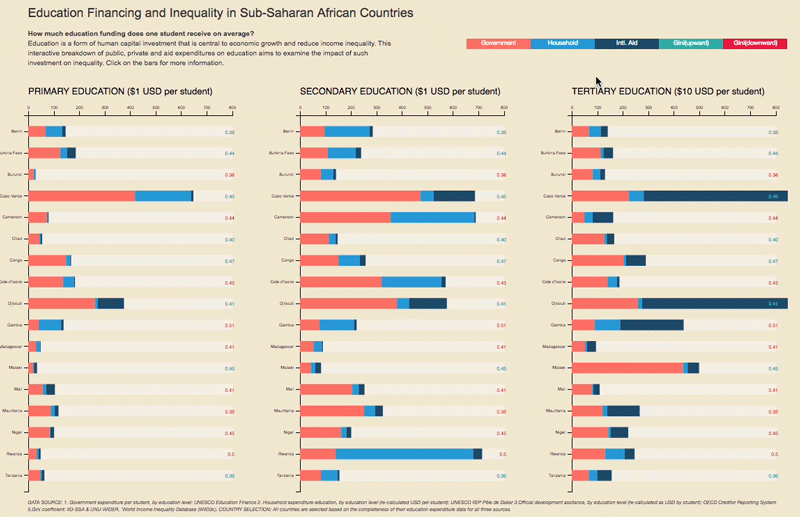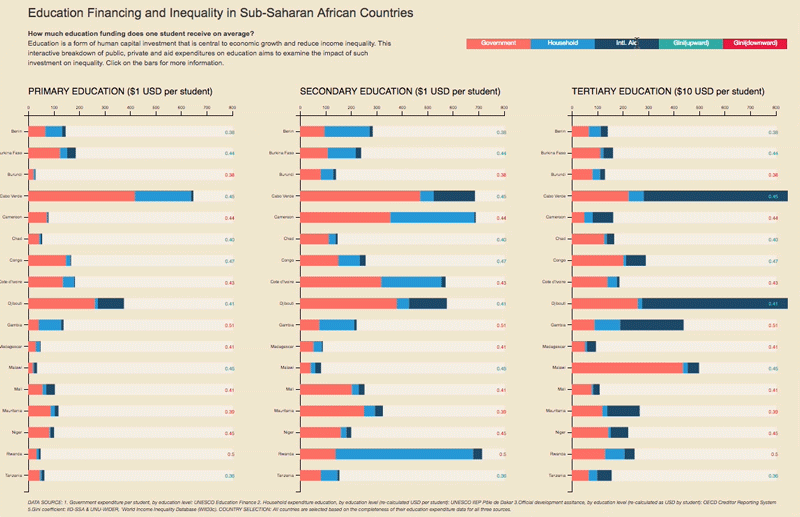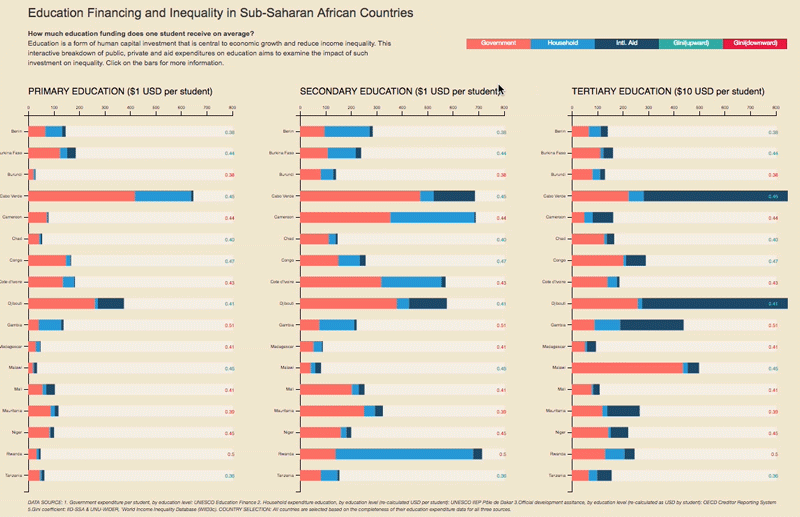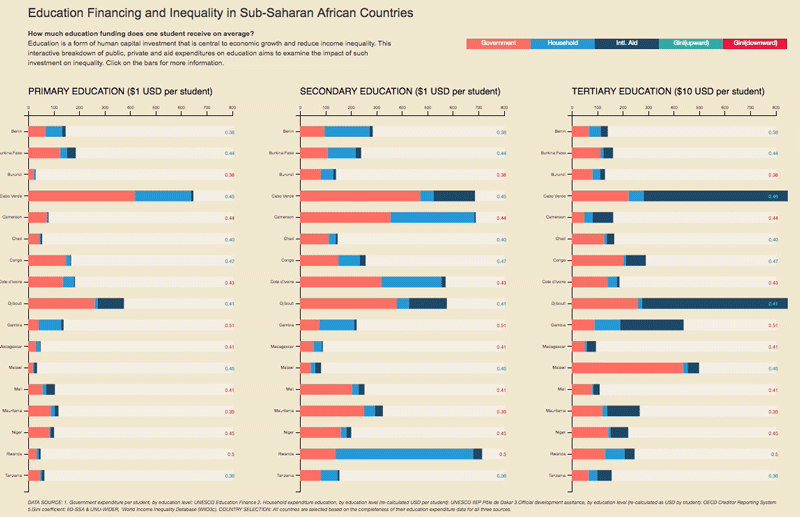
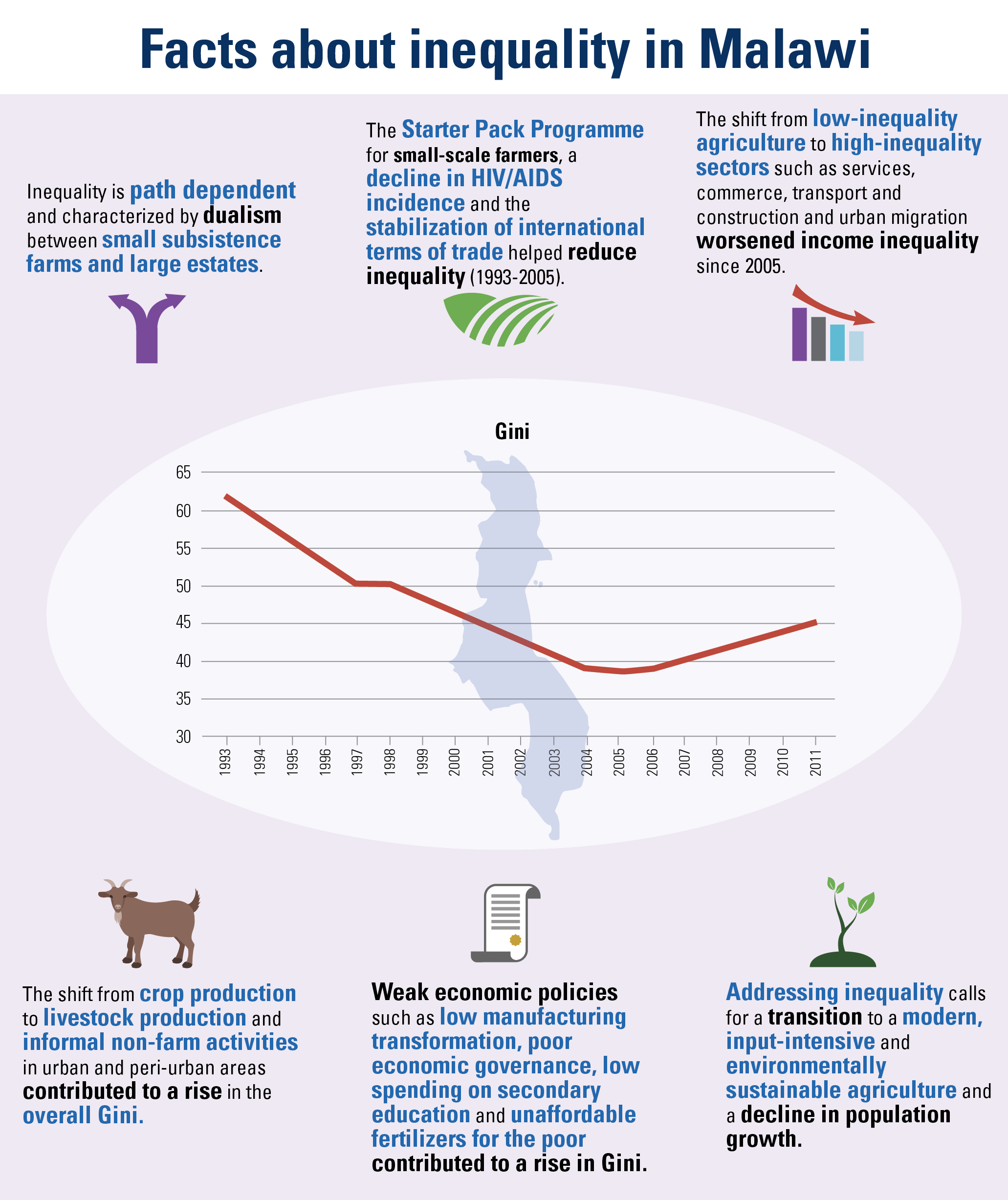
– Higher-quality education – which improves the distribution of enhanced human capital – encourages state authorities to use this increased supply to build a fairer society;
– Increased efficiency in tax administration, leading to investment in social expenditures and programmes which reduce inequality.
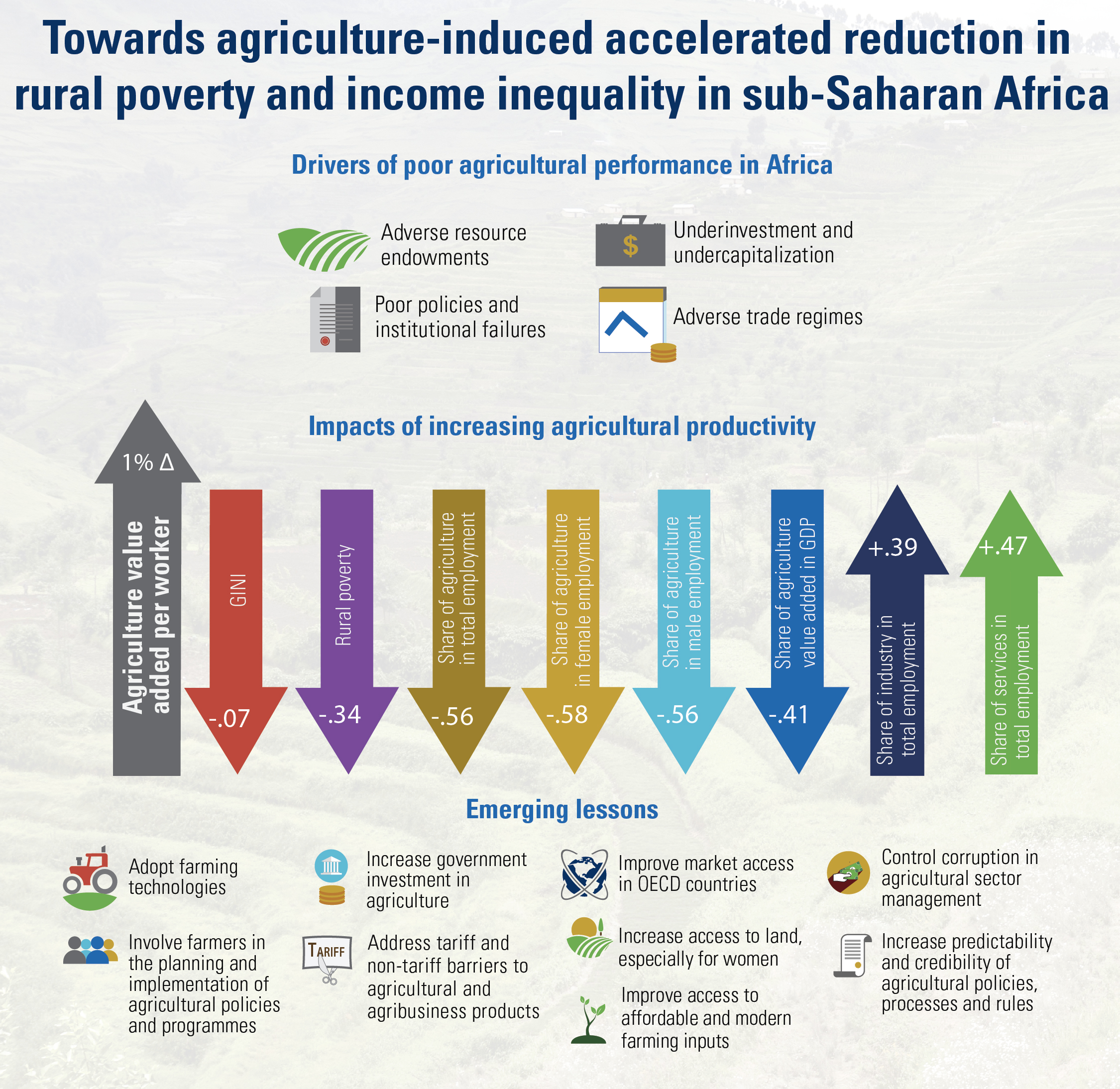
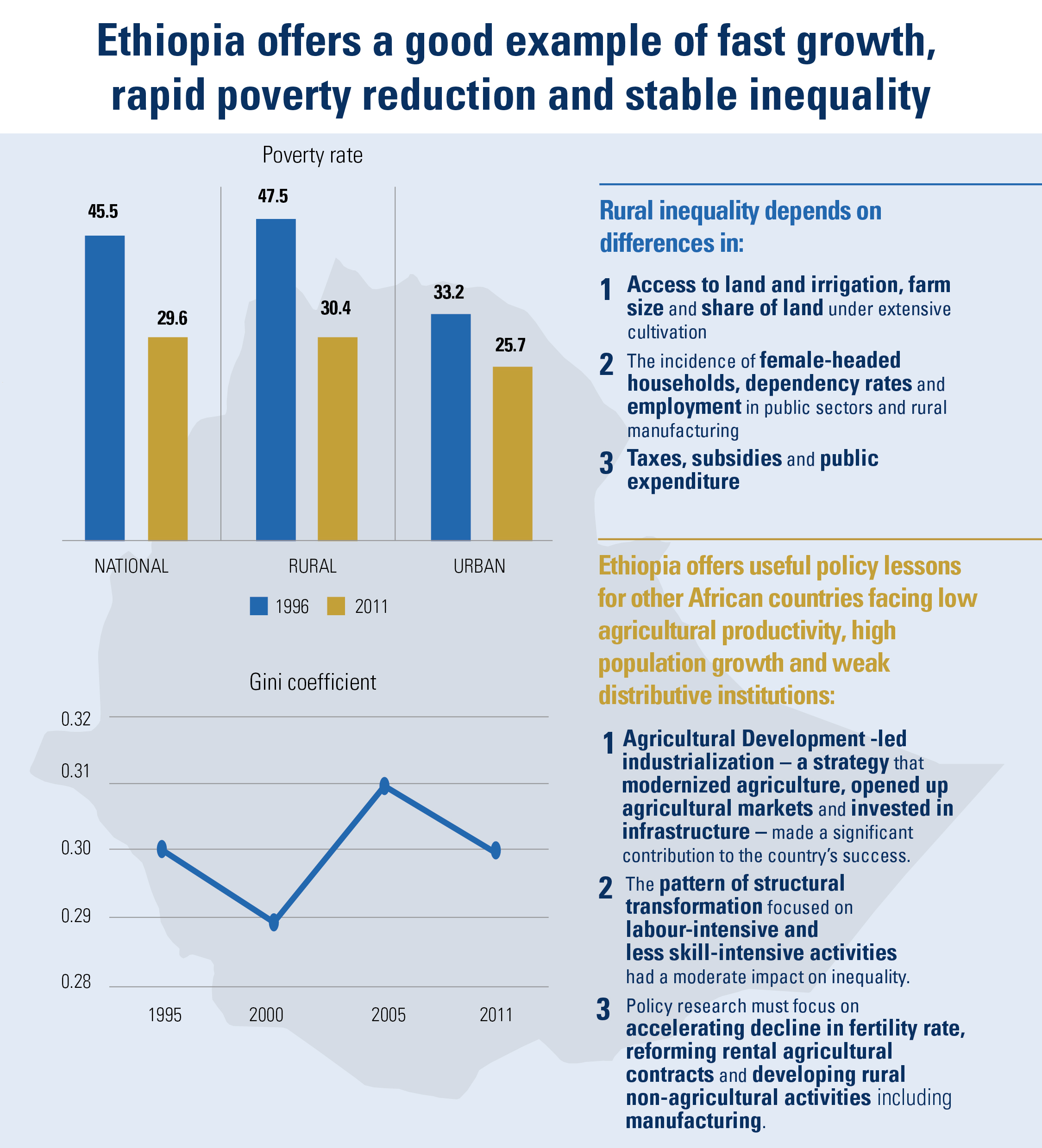
– Enhanced agricultural productivity, an important towards reallocating labour to other sectors of the economy and helping to reduce rural poverty and inequality;
– Structural transformation combined with economic diversification and infrastructure development shifts production patterns towards manufacturing and adding value to primary commodities

 Locations
Locations